SQA-006
[Paper] Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-BasedGenerative Models
We argue that the theory and practice of diffusion-based generative models arecurrently unnecessarily convoluted and seek to remedy the situation by presentinga design space that clearly separates the concrete design choices
Theory and Notations
Diffusion-like methods formulation: SDE
\[\text dx = f(t)\ x\ \text dt+g(t)\ \text dw\]With marginal $p_t=p(x\mid \sigma(t))$, where \(p_t(x)=\int p_{t0}(x\mid x_0)p_{data}(x_0)\ \text dx_0\)
And $p_{t0}(x\mid x_0)$ is the transition kernel, with \(p_{t0}(x\mid x_0)=\mathcal N(x; s(t)x_0, s(t)^2\sigma(t)^2I)\)
实际上这些参数的联系是(我不想证, 看看得了) \(s(t)=\exp\left(\int_0^tf(\xi)\text d\xi\right), \sigma(t)=\sqrt{\int_0^t \frac{g(\xi)^2}{s(\xi)^2}\text d\xi}\)
其中 $\sigma$ 就是 noise schedule, $s$ 是 scale schedule
Design Space
本文先研究 ODE sampling, 并使用了 higher order solver (heun 3阶 / Runge-Kutta RK45 2阶) 来加速 sampling
其中使用 heun 可以在很少的步数(<40)步得到最好的效果
注意: noise schedule 指一个 $\mathbb{R}^+\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^+$ 的函数, 是连续的, 它定义了 ODE; 然而我们用来求解 ODE 的 time step 并不一定是均匀的.
我们使用 $\sigma(t)$ 表示 noise schedule, 而 $\sigma_i$ 表示在 $i$-th time step 的 noise level
Time step
文中提出了 general time step choice: $\sigma$ 对应线性函数的 $\rho$ 次方
\(\sigma_i = (\sigma_{\text{max}}^{1/\rho}+\frac{i}{N-1}(\sigma_{\text{min}}^{1/\rho}-\sigma_{\text{max}}^{1/\rho}))^{\rho}\) and $\sigma_N=0$
其中文中理论分析得到, 约 $\rho=3$ 的时候, 解 ODE 时候各处的误差比较平均; 但是 practically, $5\le\rho\le10$ 之间效果比较好 (这说明对于 noise 较小的时候比较关键). 最终采用 $\rho=7$
Design of noise schedule and scale schedule
通过一通操作, 得出结论: $\sigma(t)=t, s(t)=1$ 最好
这个设计和 DDIM 吻合
Stochastic Sampling: Better quality
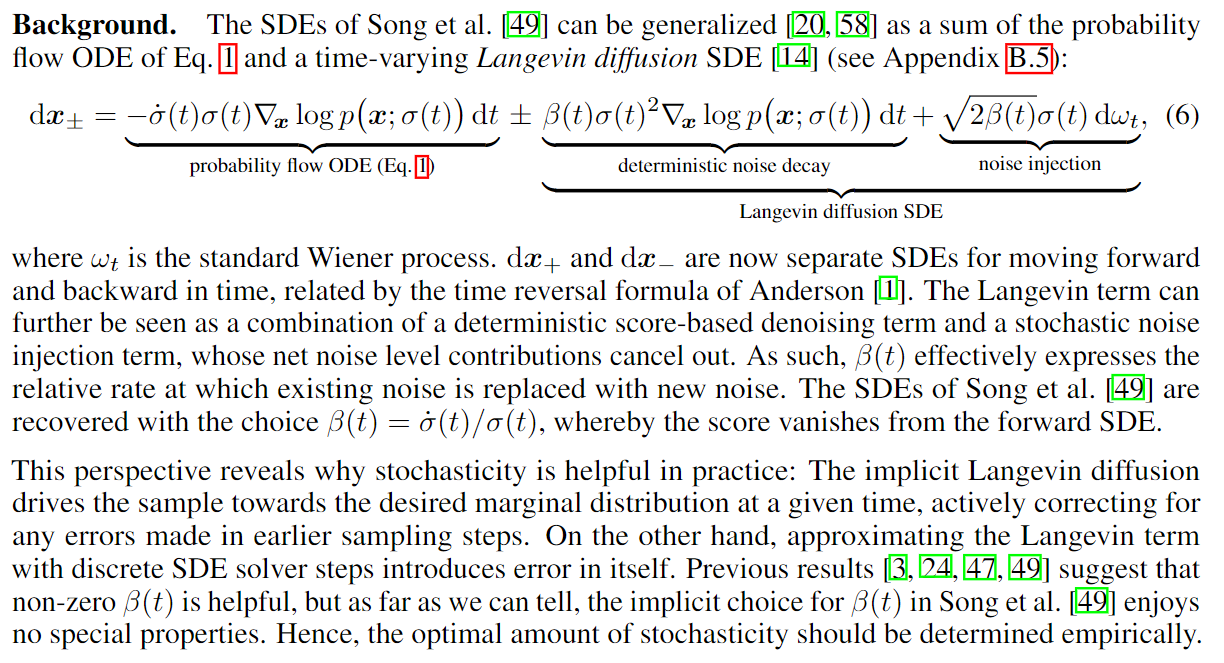
本文提出了对于 SDE 的一个新 sampler, 包含二阶修正项. 注意, 这个算法并不适用于一般的 SDE
其不加噪声的版本就是 heun, 但是对于上面提到的 time step 解.
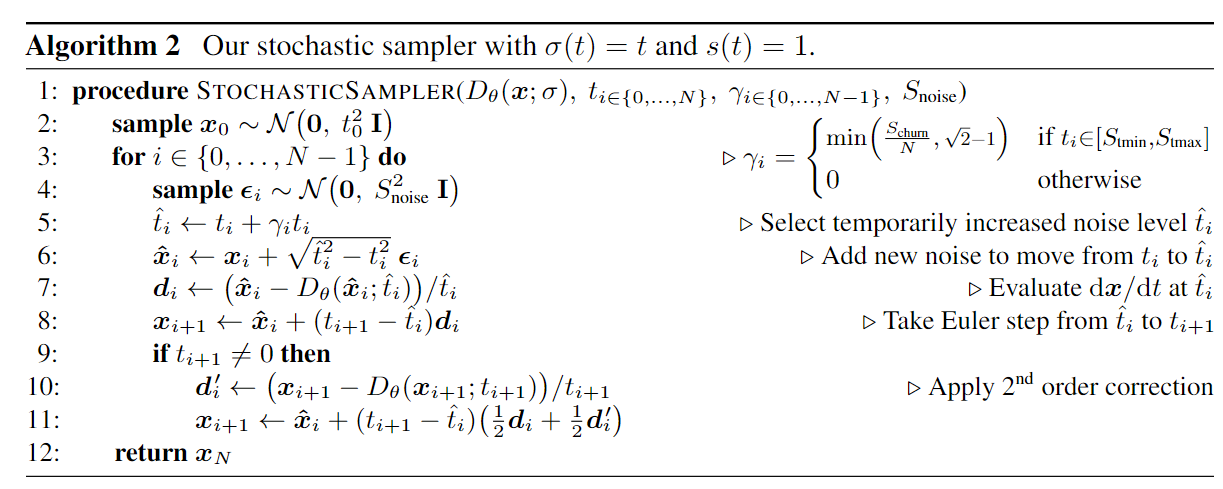
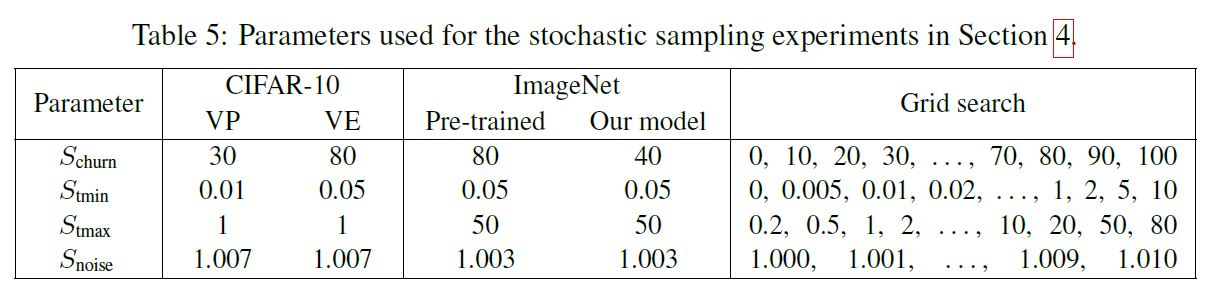
其中的深意是: 我们 SDE sample 的时候加不加噪声其实是可以自己调整的, 所以我们规定只在 $t_i\in[S_{tmin},S_{tmax}]$ 的时候加噪声. 其中加噪声的 level 由 $\gamma$ 控制 ($\gamma$ 实际上是一个比例), 其中 clip 到 $\sqrt 2$ 保证了我们不会给图片加多余自身的噪声. 最后, 这里的 $S_{noise}$ 理论上应该是 1, 但是他们搜索发现 1.007 比较好.
论文做了 1e4 的 grid search 找参数, 卡少
Practical considerations: Increasing the amount of stochasticity is effective in correcting errors made by earlier sampling steps, but it has its own drawbacks. We have observed (see Appendix E.1) that excessive Langevin-like addition and removal of noise results in gradual loss of detail in the generated images with all datasets and denoiser networks. There is also a drift toward oversaturated colors at very low and high noise levels. We suspect that practical denoisers induce a slightly non-conservative vector field in Eq. 3, violating the premises of Langevin diffusion and causing these detrimental effects. Notably, our experiments with analytical denoisers (such as the one in Figure 1b) have not shown such degradation. If the degradation is caused by flaws in $D_{\theta}(x;\sigma)$, they can only be remedied using heuristic meansduring sampling. We address the drift toward oversaturated colors by only enabling stochasticity within a specific range of noise levels $t_i\in[S_{tmin},S_{tmax}]$. For these noise levels, we define $\gamma_i=S_{churn}/N$, where $S_{churn}$ controls the overall amount of stochasticity. We further clamp $\gamma_i$ to never introduce more new noise than what is already present in the image. Finally, we have found that the loss of detail can be partially counteracted by setting $S_{noises}$ lightly above 1 to inflate the standard deviation for the newly added noise. This suggests that a major component of the hypothesizednon-conservativity of $D_{\theta}(x;\sigma)$ is a tendency to remove slightly too much noise — most likely due to regression toward the mean that can be expected to happen with any L2-trained denoiser [30].
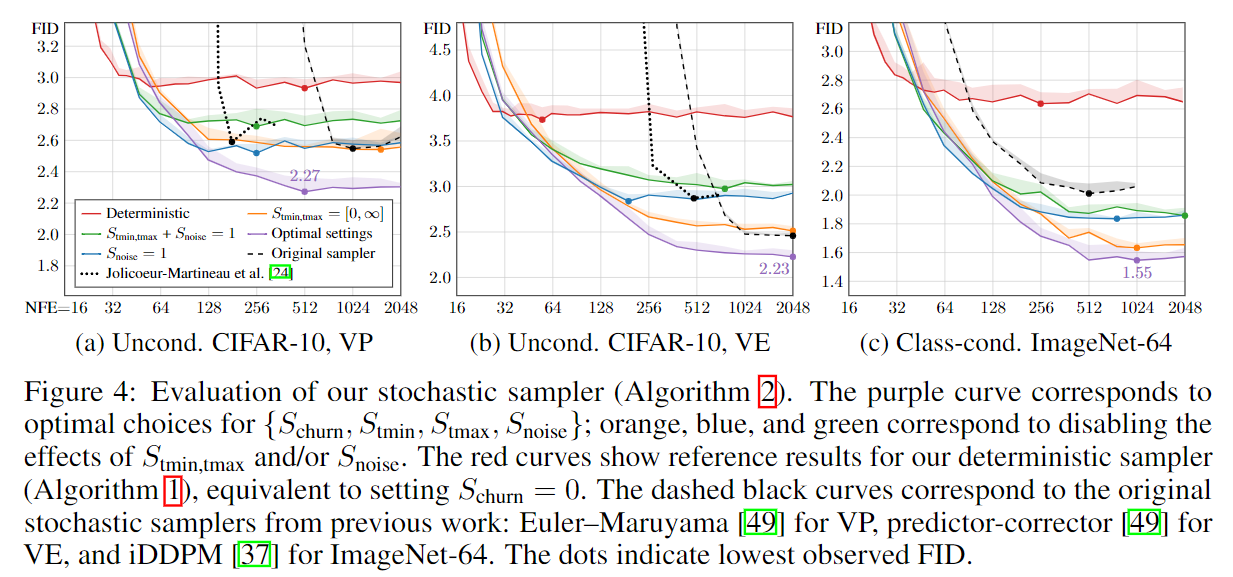
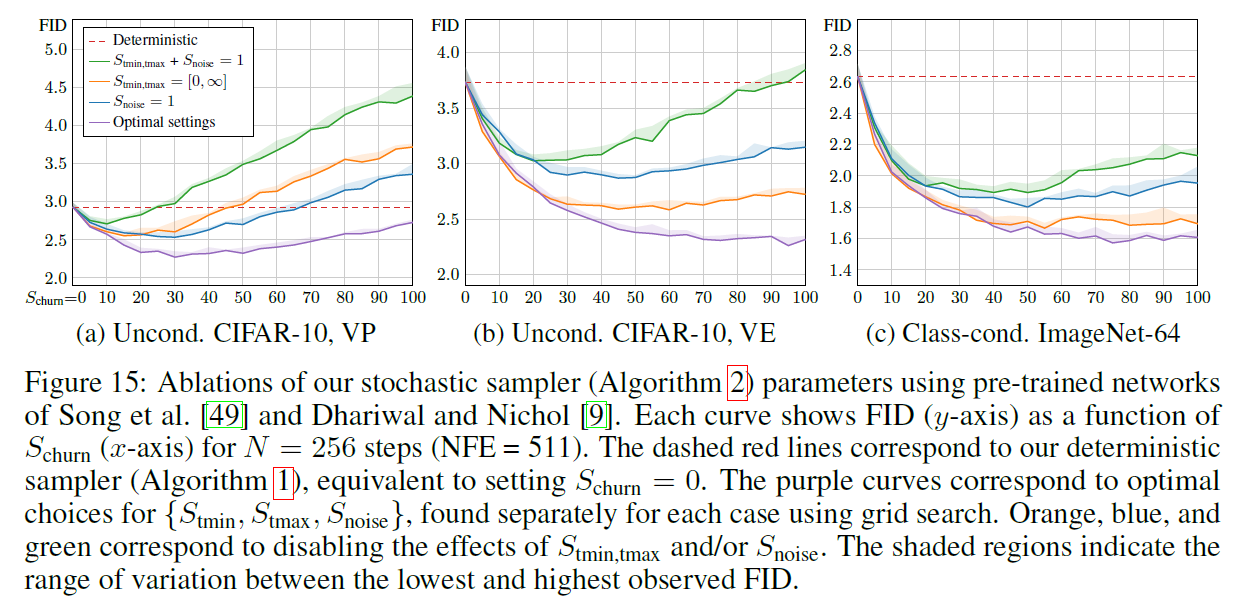
从图中可以看出, 在 步数比较少 的情况下还是 ODE 比较好, 否则 SDE 比较好
论文后面还说了, 在把模型什么的全改进了之后, SDE sampler 其实就好. 唐
Parameterization
\[D_{\theta}(x;\sigma)=c_{skip}(\sigma)x+c_{out}(\sigma)F_{\theta}(c_{in}(\sigma)x;c_{noise}(\sigma))\]with training weight $\lambda(\sigma)$. Also, training time $\sigma$ is sampled from a different distribution, call it $p_{train}(\sigma)$
- Effective weight is $\lambda(\sigma)c_{out}(\sigma)^2$, and we set it to 1
- We pick $p_{train}$ to be a log normal distribution $\ln(\sigma)\sim \mathcal N(P_{mean}, P_{std}^2)$
where mean=-1.2, std=1.2. 这一步很有深意 - 防止过拟合, 采用了 GAN 类似的 data augmentation, with aug label. 这一步也很有深意
以上这些东西设置下, stochastic sampling 也还是更好, 而 ODE 也变好了
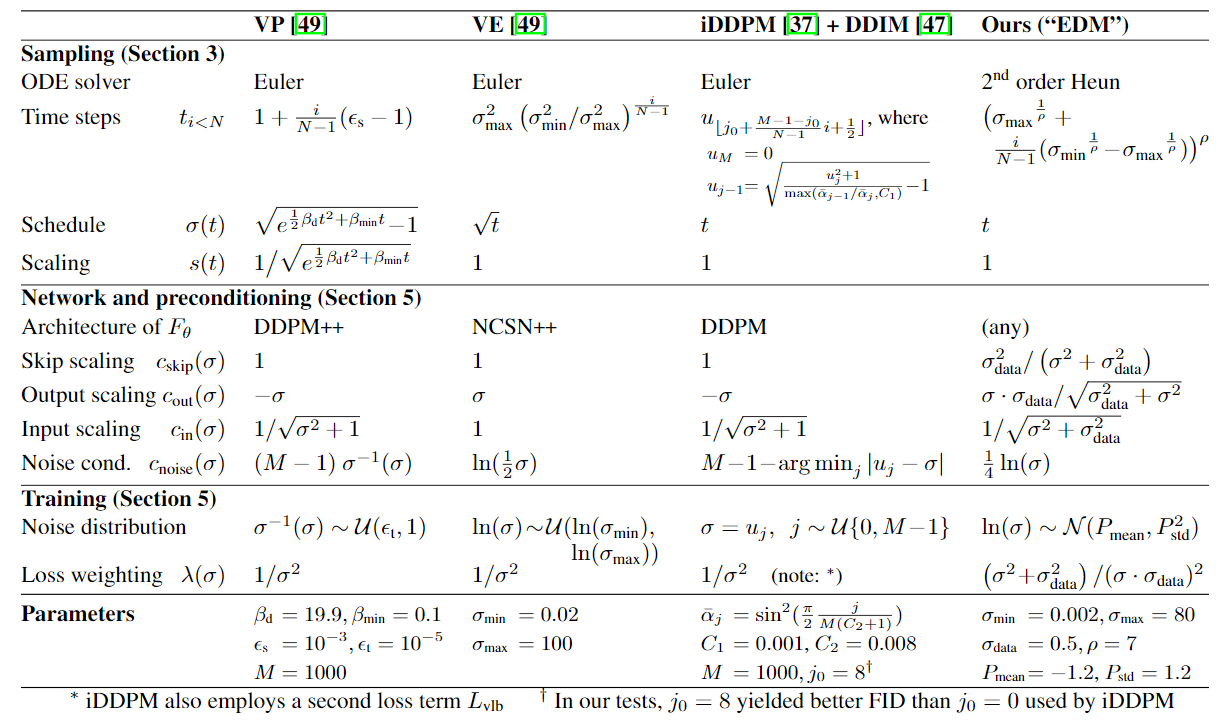
这些参数的来源: 让输入网络的东西 variance=1; 以及让目标 variance=1
最后再让 $c_{out}(\sigma)$ 最小, 这样误差比较小
- 把网络的最后一层输出层初始化成 0
真是卡多
Appendix: more
ODE sampler
文中提出了二阶 sampler 的一般形式 (他们把这个叫成 second-order Runge-Kutta variant)

其中 $\alpha$ 是一个可以调的参数. 经过卡少的测试, 发现 $\alpha$ 接近 1 (实际上 1.1) 的时候最好, 而这正好对应 heun. 作者对此解释不多, 不如直接用 heun 得了.
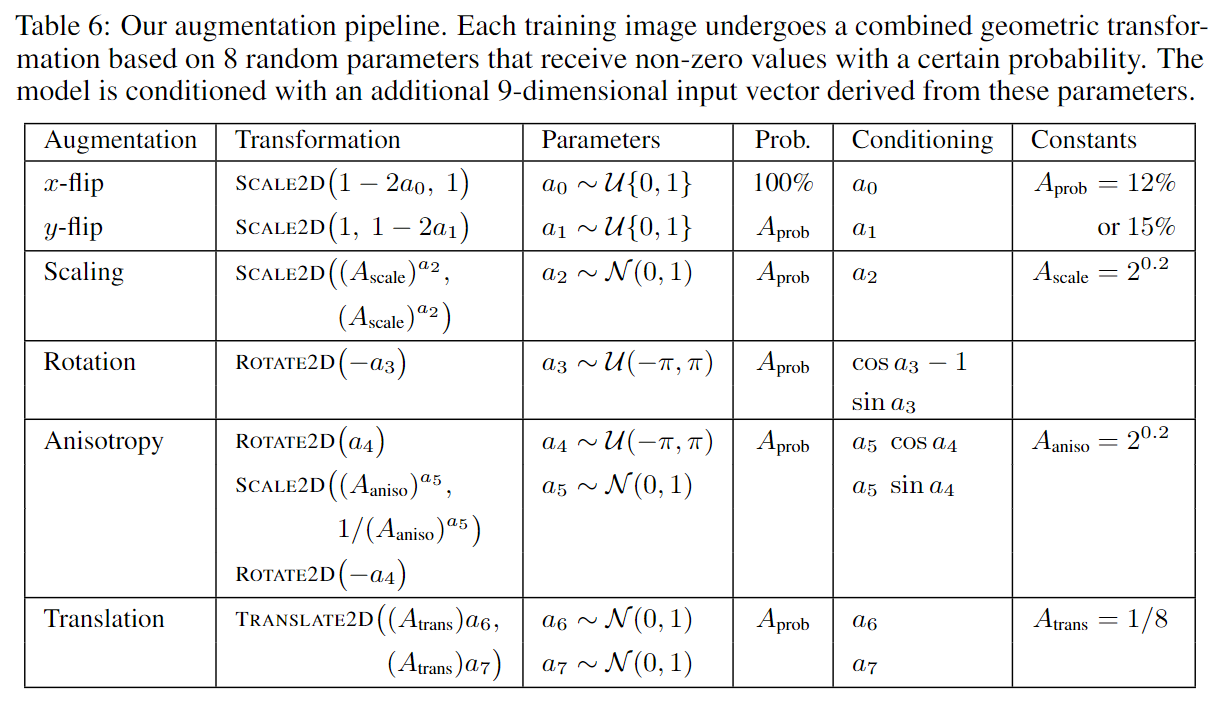
Augmentation
论文提到, 某些 augmentation 对 diffusion model 十分有害, 比如 color corruption & image-space filtering